Usage of English Tenses – Important English Grammar Tricks
Now a days Exams has changing the questions pattern of English Section more often, to tackle the English Section aspirants should be very strong in the Basic English Grammar. To help you in this aspect here we have given the Important English Grammar Tips in usage of English Tenses which will be more helpful to attend Error Spotting Questions
ENGLISH TENSES
V1=present tense verb
V2 =past tense verb
V3 =past participle
V4= present participle / V1+ing
S= subject
O= object
M.A=modal auxiliaries
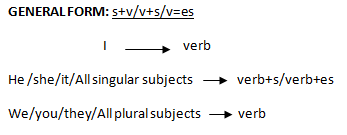
USAGE OF ENGLISH TENSES
| Tense | Format | Example |
| Simple present tense | (i)S+be form(present)+c…(ii) S+v1+o | (i)I am a tutor.(ii)I write a letter. |
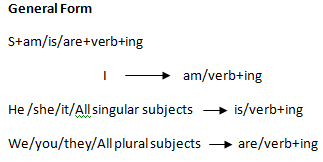
| Present continuous tense | S+be form (pr)+v4+o | I am writing a letter. |
| Present perfect tense | S+have/has+v3+o | I have written a letter. |
| Present perfect continuous tense | S+have/has+been+v4+o | I have been writing a letter. |
| Simple past tense | (i)s+be form past+c…(ii) s+v2+o | (i)I was a tutor.(ii) I wrote a letter. |
| Past continuous tense | S+be form (past)+v4+o | I was writing a letter. |
| Past perfect tense | S+had +v3+o | I had written a letter. |
| Past perfect continuous tense | S+have/had+been+v4+o | I had been writing a letter. |
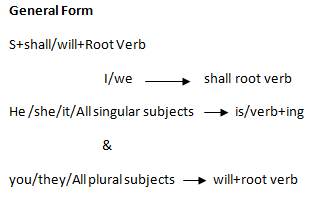
| Simple future tense | (i)S+m.a+be+….(ii)s+m.a+v1=o | (i)i will be there at 11am.(ii) I will write a letter. |
| Future continuous tense | S+m.a+be+v4+o | I will be writing a letter. |
| Future prefect tense | S+m.a+have+v3+o | I will have written a letter. |
| Future perfect continuous tense | S+m.a+have+been+v4+o | I will have been writing a letter. |
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: It is called the tense of science because all the scientific and universal truths are expressed in simple present tense.
KEYWORDS:
Usually, often, as usual, ever, in general, Frequently, generally, sometimes, always, in these days, Rarely, regularly, seldom, as a rule, occasionally, Normally, Hardly ever, periodically, scarcely, Now- a- days, Daily, in modern days, every time, never, every day, Every week, Every month, Every year, once, twice/in a week…
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE:
A)Used to express a regular, habitual, or repeated actions or events.
Eg: He takes the dog out twice a day.
B)To express a universal truth or scientific principle.
Eg: The planets revolve round the sun.
C)To express a future action(pre-planned action).
Eg: The Governor arrives here tomorrow morning.
D)Used in proverbs and maxims.
Eg: Honesty is the best policy.
E)Used to express Future tense after conjunctions showing time.
Eg: Wait here till I return.
F)Used in imperative sentences.
Eg: Write neatly.
G)To tell about Past events in a dramatic way.
Eg: Now King Porus leads his army and attacks Alexander.
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
An action that is happening continuously at present can be expressed in present continuous tense.
Keywords
Now, still, always, At present, still now, presently, At this moment, even now, any longer, Any more
Example
She is going to be married next month.
My uncle is going to Chennai tomorrow.
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
It is used to refer the action completed recently.
Example
- Used to indicate actions completed in the immediate past, the present perfect tense with the adverb “Just” may be used.
He has just gone out.
- Used to refer to experiences for which no definite time/date in the past need to be given.
I have always spoken the truth.
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
It can be used to refer an action that began in the past, happening in the present and will continue in future.
Keywords
Since, for
Examples
We have been working hard for the examination for three months.
It has been raining heavily since last evening
SIMPLE PAST TENSE
It is used to express an action, which took place in the past and is completed by the time of speaking.
Keywords
Yesterday, last week, last month, Last year, ago, once, Once upon a time, in those days, one day, Then, since, in olden days, In ancient times, in early days, in my childhood, In my boyhood days, long long ago, two years ago
Examples
Our School celebrated its Silver Jubilee last month.
We got Independence on 15th August 1947.
PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
Used to refer an action has happening at a particular point of time in the past.
Keywords
All last night, from two o’clock to four, All morning yesterday, at 9 o’clock this morning, For a long time yesterday, throughout the night
Examples
- Used to express an action going on at sometime in the past.
It was raining throughout the night.
- Subordinate clause that starts with ‘While’ can be used Past Continuous Tense.
While Bama was dancing, she fell down.
- If two actions occur simultaneously both the actions should be mentioned in Past Continuous Tense.
While my mother was cooking, my father was listening to the radio.
- Two action occur in the past one action is completed before the other starts. The first completed action is in Past Continuous Tense and the other is Simple Past Tense.
I was reading when he came in.
PAST PERFECT TENSE
It can be used to refer two actions in the past. The first completed action should be in Past Perfect and the next one should be in the Simple Past Tense.
General Form
S+had+Past Participle
Examples
- Subordinate clause that starts with ‘After’ should be in Past Perfect Tense.
After the tailor had taken the measurements, he cut the clothes.
- Subordinate clause that starts with ‘Before’ should be in Simple past and the main clause should be in Past Perfect.
We had reached home before it began to rain.
- Used to describe an action completed before a certain period/point of time in the past.
We had taken our dinner by eight o’clock.
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Used to refer the actions that happened in the past for a particular period but not now.
General Form
S+had+been+verb+ing
Keywords
Since, for
Examples
When I met him in 1950 he had been living in Chennai for five years.
Ha had been teaching English
SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
Way of referring future time.
Keywords
Tomorrow, in future, Next week, early, Next month, next Monday,
Soon, in a few minutes, Shortly, in the coming days, In 2018, later, Hereafter, this evening,
In a little time, in the years to come, Within a week
Examples
We shall buy a T.V. next month.
You will know the result in a week.
FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
Used to indicate the completion of an action before a given time in the future.
General Form
S+shall/will+be+verb+ing
Keywords
By this time tomorrow, At this time tomorrow, During July and August, By 3 o’clock tomorrow
Examples
He will be travelling all the morning tomorrow.
My father will be reading the newspaper at 8 a.m. tomorrow.
FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
Used to refer an action that will be expected of its completion at a particular time in the future.
General Form
S+shall/will+have+Past Participle
Keywords
By the end of this year, By this time tomorrow, In two years time, In July next year, In another five months
Examples
By April next year, I Shall have completed the 10th standard.
The classes will have begun by the time you reach school.
FUTURE PERFFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Used to refer the action that will begin in the future and will be happening continuously.
General Form
S+shall/will+have+been+verb+ing
Keywords
By the end of this year, By this time tomorrow, In two years time, In July next year, In another five months
Examples
She will have been living in Delhi for five years by the end of this month.
He will have been serving this school for ten years when he retires from service.
Below we have given some exercise questions which may consist of errors (based on above notes), check whether the statement has error or not if any give your answers in the below comment section.
Exercise Questions:
1) Is your parents coming for the festival?
2) It is him that I have been looking for.
3) Being a nice day, we decided to go out.
4) The horse and carriage are at the door.
5) He is one of the servants who hardly ever works.
6) He would sooner to quit the job than bear such insult.
7) My friend and brother have come.
8) The courtyard is infested by flies.
9) Learn respecting your parents.
10) The crowd have to answer to what the culprit says.
11) He denied that he was not a thief.
12) He dares not to commit a murder.
13) The three-member bench was divided in its verdict.
14) This made me think of the time went by.
15) You have joined us with a view to improve your English.
16) Thirty kilometres are a big distance.
17) He works as if today is the last day of his life.
18) Let us go to seeing the bride.
19) The news are being broadcast to you from the All India Radio.
20) I am seeing a rainbow in the sky.
EXPLANATION:
1). Parents – father and mother. Parent – only one of the two. So, are your parents coming for the festival?
2). The complement of the verb to be , when it is expressed by a pronoun, should be in the nominative( subject) form. ‘ Is’ is aform of to be. ‘Him’, which is in the objective case, should therefore be changed to ‘he’. So, it is he that I have been looking for.
3). The sentence gives the impression that ‘being’ is the participle used for the pronoun ‘we’. So, we may not say ‘we are a nice day’. It is absurd. We must use the pronoun ‘it’ in this place. So, It being a n ice day, we decided to go out.
4). ‘The horse and carriage’, is together and a part of a(one) system. So, a singular verb is required. Note that, article “the” is used only once in a sentence means it is a whole system together. If the is used twice (the horse and the carriage) means two parts. So the horse and carriage is at the door.
5). The relative pronoun who does not refer to one, but to servants. So, the verb should be plural. So, He is one of the servants who hardly over work.
6). Would sooner is followed by an infinitive without to. So, He would sooner quit the job than bear such insult.
7). If two persons were being talked about, the sentence would go as follows: My friend and my brother….. As it is, we conclude that one man is being talked about who is both ‘My friend’ and ‘my brother’. Hence the verb takes singular form. So, my friend and brother have come.
8). ‘Infested with’ is the correct form. So, the courtyard is infested with flies.
9). Learn is followed by the infinitive. So, learn to respect your parents.
10). ‘The crowd’ is a collective noun. So, it takes singular verb. So, the crowd has no answer to what the culprit says.
11). Denied means ‘to declare untrue’ is a negative word so it is not necessary to add one more negative not to it. So, He denied that he was a thief.
12). Dare is followed by an infinitive without to. So, He dares not commit a murder.
13). ‘Three member bench’ is collective noun but the members in it behave variously because the verdict is different. So, the verb takes plural form. So, the three-member bench were divided in its verdict.
14). The action of going is not continuous, but over, we should use past participle. So, this made me think of the time gone by.
15). ‘To improve’ here should not be viewed as an infinitive. The ‘to’ before improve is actually a part of the phrase with a view to. This phrase should be followed by a gerund, not an infinitive. So, you have us with a view to improving your English.
16). The sentence is giving the fact. So, several distances give the fact of a single distance sense. It takes singular form and singular verb. So, thirty kilometres is a big distance.
17). Considering the mood and emotion of the sentence ‘is’ is not the appropriate form of ‘be’ here. The past subjunctive of ‘be’ is ‘were’. So, He works as if today were the last day of his life.
18). To express the purpose of going, should use ‘to see’. So, Let us go to see the bride.
19). News is usually treated as singular. So, the news is being broadcasted to you from the All India Radio.
20). Rainbow would exist for a short span. So we may not use continuous tense. Simple present tense is the correct tense form. So, I see a rainbow in the sky.
Subscribe Our YouTube Channel – IdeticEdu